https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tUEMC42xjrY
This new budget bill brings several changes, especially concerning taxes and benefits that affect individuals and families. While personal income tax rates will remain lower than previously scheduled, critics highlight potential drawbacks, particularly for Medicaid and food assistance programs. The bill introduces new work requirements for some benefit recipients and includes various adjustments to tax deductions and credits aimed at improving family finances.
Key Provisions of the New Budget Bill
Personal Income Tax
Retention of Lower Rates:
Personal income tax rates will stay lower than the rates set to revert back.
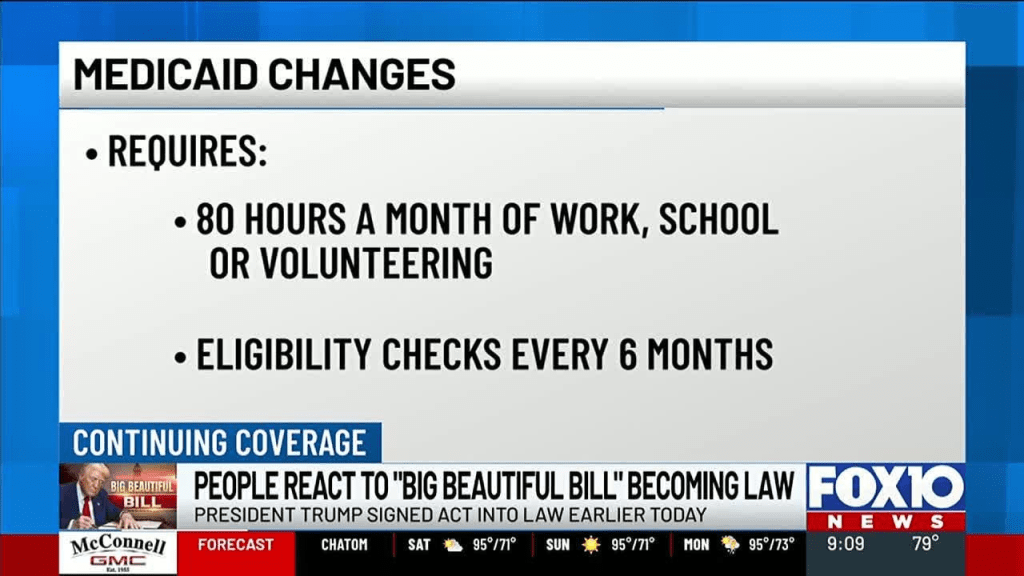
Medicaid Changes
Eligibility Requirements:
The bill does not change income eligibility but imposes new work requirements for able-bodied recipients, requiring 80 hours of work, school, or volunteering per month.
States must check eligibility every six months to prevent double enrollment and remove non-qualified individuals.
Food Assistance Program Adjustments
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP):
Similar to Medicaid, the bill maintains existing eligibility but adds work requirements for able-bodied recipients.
Expands upper age limits for work requirements from 54 to 64.
Exempts pregnant women and parents with children under 14.
Tax Benefits and Deductions
Deductions for Tips and Overtime:
Taxpayers can deduct tips (up to $25,000) and overtime earnings (up to $12,500) with income phased out for higher earners.
Changes to Child and Standard Deductions:
Standard deduction increases from $15,000 to $15,750 for singles and from $30,000 to $31,500 for couples, automatically adjusting with inflation.
Child tax credit increases from $2,000 to $2,200, also indexed for inflation.
Additional Initiatives
Trump Accounts:
A new savings program for all babies born in the U.S. during his second term, with an initial government contribution of $1,000 and a family contribution cap of $5,000 yearly. Access to funds is restricted until the child turns 18.
Criticisms of the Bill
Healthcare Concerns:
Critics argue that around 12 million people could lose Medicaid.
The new work requirements may disproportionately affect those with disabilities.
Tax Cuts for Wealthy:
Critics point out that while tax cuts for high earners are made permanent, those benefiting service industry workers are set to expire in 2028.
Key Takeaways
Personal income tax rates will remain lower.
New work requirements for Medicaid and SNAP recipients could lead to significant cuts in benefits.
Changes to tax deductions and credits aim to support families financially.
The bill’s critics are worried about the impact on healthcare and potential inequities in tax cuts.
Additional savings initiatives for newborns are introduced, encouraging future financial planning.
Summarized by Dictationer.
Try Transcribe, Summarize and Translate Anything you want.
https://www.dictationer.com/paste-link/youtube-summary
Leave a comment